Troubleshooting intermittent or no Wi-Fi connection
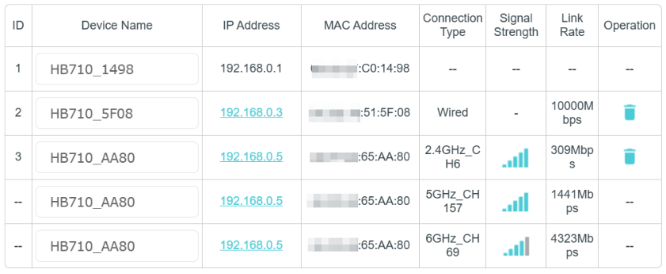
1. Monitor Link Rate and Signal Strength:
- Check the link rate and RSSI/Signal Strength of your device via the router/AP node in WebUI or Aginet APP.
- If the link rate is low or the RSSI/Signal Strength value is too low, this could cause an unstable connection. Try moving the device closer to the router/AP node and monitor again.
- Wi-Fi Signal Strength value rating table as below:
|
Signal Strength (dBm) |
Rating |
Description |
|
-30 to -50 |
Excellent |
Perfect or near-perfect signal strength. Online activities can be carried out seamlessly without fear of disconnection. |
|
-51 to -60 |
Good |
High signal strength. Good enough for most online activities, including high-intensity gaming and video streaming. |
|
-61 to -70 |
Fair |
Decent signal strength. Sufficient for everyday tasks like emails and Web surfing. |
|
-71 to -80 |
Poor |
Low level of connectivity. There may be occasional disconnects and data loss. |
|
-81 or lower |
Very weak |
Near-complete disconnection. Data loss and mid-task disconnections are frequent. |
2. Address Blind Spots:
- If there are blind spots due to the main router’s coverage limitations, consider adding another mesh node to extend the wireless coverage.
- Place the router/AP node in an area with fewer obstacles, avoid placing it on the floor, and place it high off the ground to minimize transmission interference.
3. Check Backhaul Link Rate:
- Verify the wireless backhaul link rate/signal strength between the router and the wireless mesh AP node. If it’s too low, adjust the node’s placement to ensure a more stable link rate/signal strength.
- Recommendation for backhaul signal strength: Web UI displays 4 bars and above, and Aginet APP displays green color signal strength.
WebUI:
Aginet APP:

4. Wired Connection Test:
- Connect the device directly to the ONT modem to check for any drop or instability in the internet connection from the backhaul.
- Also, check the LED status of the router/ONT modem.
- If issues persist, report the unstable internet backhaul to your service provider.
5. Unique SSID Names:
- Avoid using the same Wi-Fi SSID name for the separate 2.4GHz, 5GHz, 6GHz, and MLO Wi-Fi bands.
6. Check Power Saving Mode:
- If devices are in power-saving mode, disable them and monitor their performance, as this might be causing the issue.
7. Channel Congestion:
- For potential environmental with 2.4GHz Wi-Fi channel congestion, try switching to another channel with a lower channel width in WebUI or Aginet APP settings and monitor again.
- Channel congestion status can be checked via third party APP that is related with Wi-Fi performance, and it will show the status as below, for example:

8. Compatibility Issues:
- Some older devices may not be compatible with BE mode and higher security encryption standards. Adjust the Wi-Fi band settings to 802.11 b/g/n/ac/ax (without BE) and use lower security, such as WPA2-PSK only.
Is this faq useful?
Your feedback helps improve this site.
TP-Link Community
Still need help? Search for answers, ask questions, and get help from TP-Link experts and other users around the world.
